Side Effects Of Dabigatran Vs Warfarin

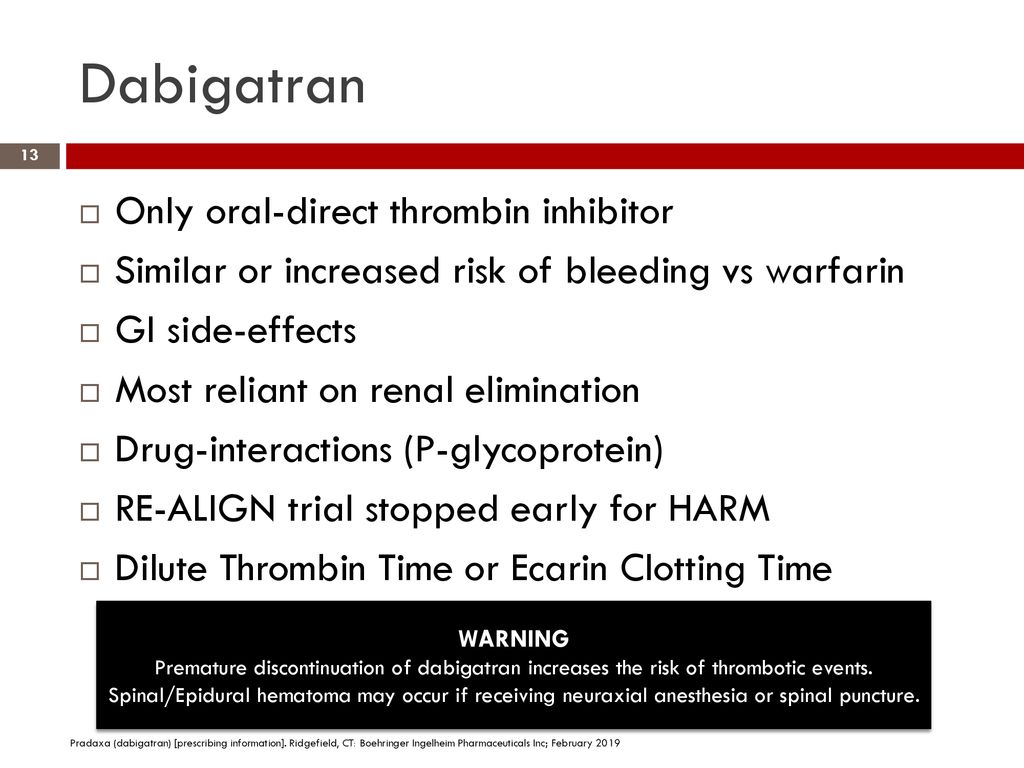
However an antidote is yet to be successfully fixed for pradaxa to ensure it is the best blood thinner that could be taken as medication.
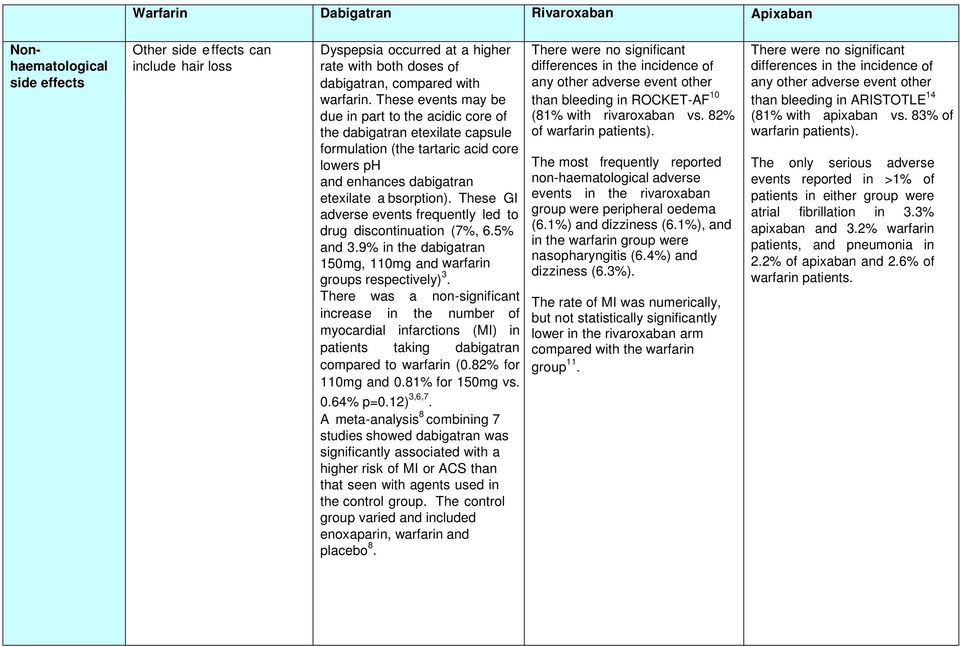
Side effects of dabigatran vs warfarin. Know the warning signs and how to prevent side effects. Current studies state that pradaxa as a blood thinner has more manageable side effects. Compare pradaxa vs warfarin head to head with other drugs for uses ratings cost side effects interactions and more. Compare coumadin vs pradaxa head to head with other drugs for uses ratings cost side effects interactions and more.
Dabigatran carries an approximately 10 percent risk of heartburn so severe that patients have to switch drugs noseworthy says. Pradaxa is used to. Studies show the latest drugs work as well as warfarin. For those on warfarin that drug s.
Pradaxa could be the best alternative blood thinner medication with fewer side effects. You may report side effects to fda at 1 800 fda 1088. By mayo clinic staff. But trying to figure out how the new medicines compare to each other is a bit trickier.
Although commonly used to treat blood clots warfarin coumadin jantoven can have dangerous side effects and put you at risk of heavy bleeding. They are also used to treat these conditions if they develop. Pradaxa rated 7 1 10 vs warfarin rated 8 2 10 in overall patient satisfaction. Reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in people who have a medical condition called atrial fibrillation not caused by a heart valve problem.
Pradaxa dabigatran etexilate capsules is a prescription blood thinner medicine that lowers the chance of blood clots forming in your body. This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Rates of the primary outcome were 1 69 per year in the warfarin group as compared with 1 53 per year in the group that received 110 mg of dabigatran relative risk with dabigatran 0 91. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
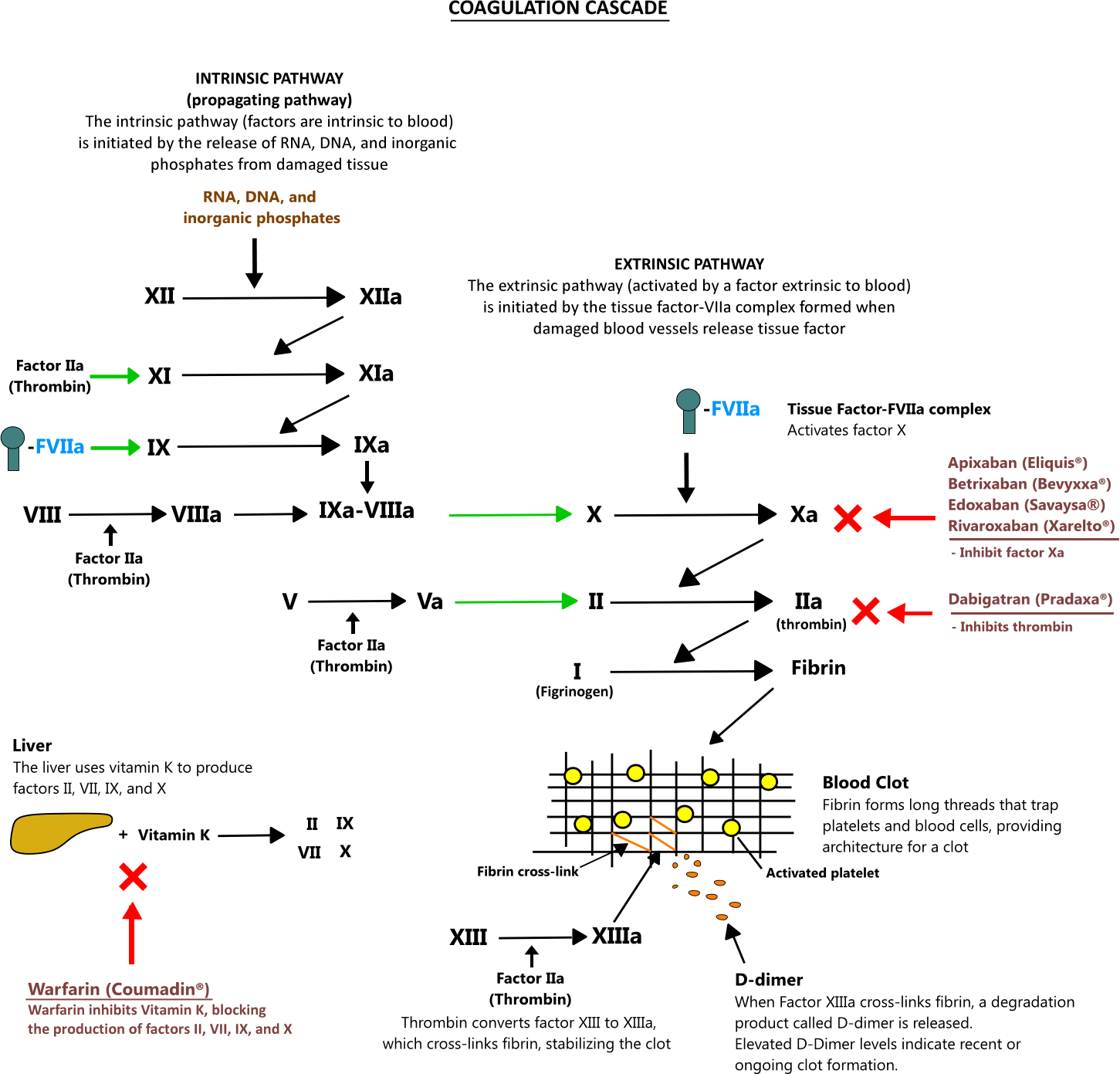
Pradaxa dabigatran and coumadin warfarin are anticoagulants used to prevent blood clots to reduce or prevent the chance of developing heart attacks myocardial infarctions strokes and venous and other blood clots deep venous thromboses pulmonary emboli and thrombi produced with atrial fibrillation.